Global Indoor Health Network
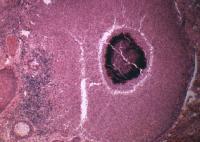
Actinomycetes sulfur granule
The Global Indoor Health Network is a 501(c)(3) organization dedicated to providing education and awareness of the health effects of mold and other indoor contaminants. Our worldwide network of experts and laypersons are working together to promote healthy indoor environments in homes, schools and businesses.
FAIR USE NOTICE: This site may contain copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. We are making such material available in our efforts to advance the understanding of environmental, political, human rights, economic, democracy, scientific and social justice issues. We believe this constitutes a 'fair use' of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes.
DISCLAIMER: The contents of this website (including text, graphics and images) are for informational purposes only and do not constitute medical advice. The content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
All Rights Reserved | Global Indoor Health Network, Inc.