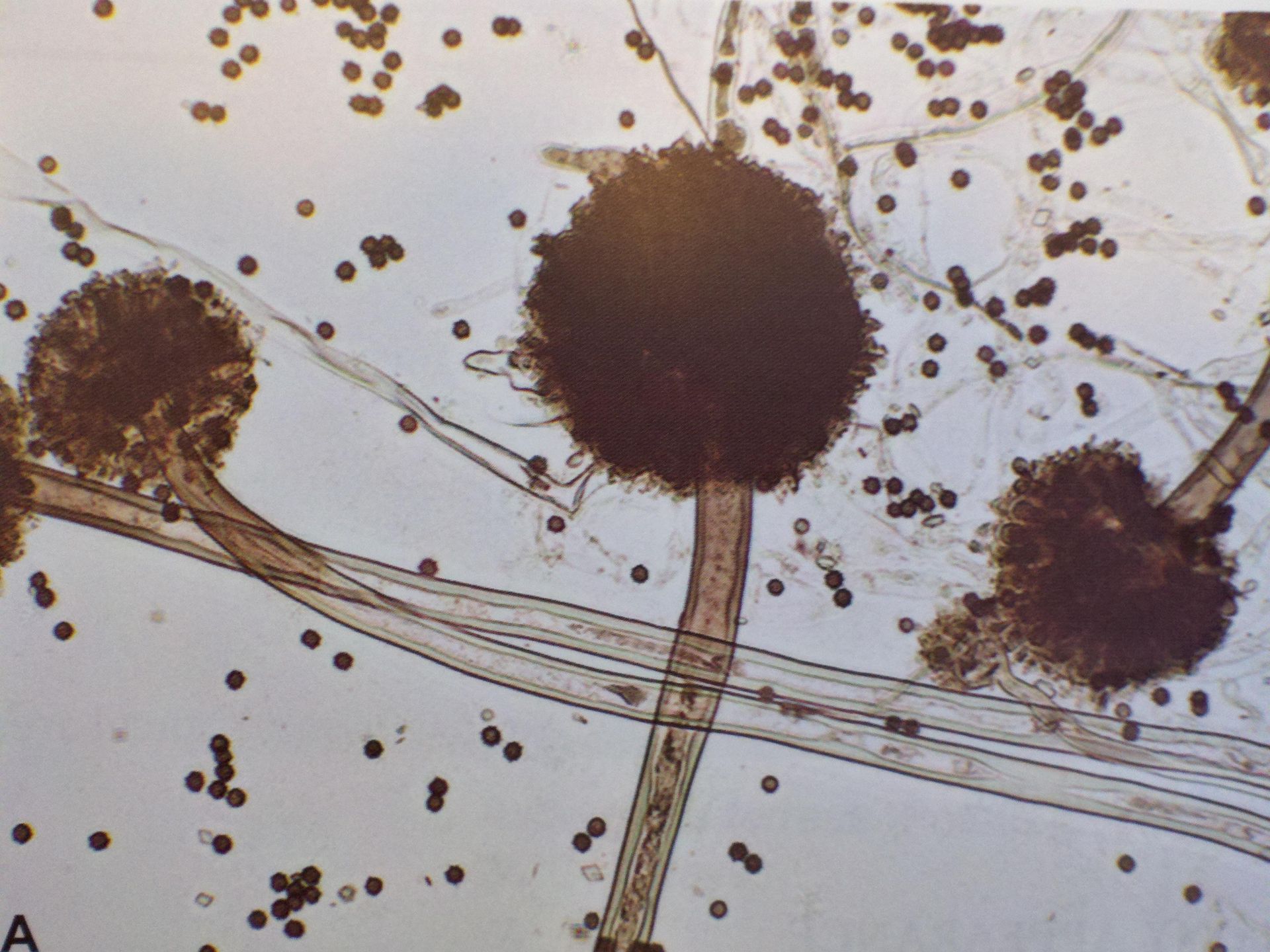
Aspergillus contains several species that are found in the environment. Some are pathogenic to plants, animals and humans. In addition, several species produce mycotoxins. These mycotoxin-producing species are present in damp indoor spaces. Therefore, only those species commonly found in damp indoor spaces will be discussed here.
Aspergillus flavus
A. flavus has been detected in damp indoor spaces by PCR DNA (ERMI Test) and by culture on Malt Extract Agar (MEA) plates.
Its optimum temperature for culture is 37 °C. Thus, it is recommended that cultures of molds be carried out at both 37 and 28 °C. A. flavus and a few other Aspergillus species will grow readily at this temperature, while Penicillium spp. and other genera will grow out rapidly at 28 °C, crowding out and masking the identification of A. flavus.
This species produces Aflatoxins B1, B2, and the animal metabolite M1. M1 has been detected in the milk of humans and animals that presumably consumed contaminated grain. In addition, Hooper et al (2009) have reported Aflatoxins in tissue biopsy/autopsy and urine from humans exposed in to Aspergillus spp in damp indoor spaces. Read the paper.
Aflatoxin B1 is carcinogenic and adducts to the guanine basis. In addition, it readily adducts to proteins, particularly serum album. Antibodies to aflatoxin-albumin adducts have been demonstrated in humans.
Hepatocellular carcinoma has been associated with Aflatoxin B1 and individuals with Hepatitis B are more susceptible to the carcinogenic effects of this mycotoxin.
Finally, A. flavus has been shown to produce gliotoxin and has been detected in the sera of cancer patients with aspergillosis as well as in mice with aspergillosis.
Aspergillus versicolor
This species produces Gliotoxin, Cyclopiazonic acid, Sterigmatocystin and Methoxy Sterigmatocystin. Cyclopiazonic acid is acutely toxic to rats. Intraperitoneal injection produces hyperesthesia and convulsions followed by death in about 30 min. The LD50 in males is 2.3 mg/kg.
Oral administration results in death in 1–5 days with an LD50 of 36 mg/kg in males and 63 mg/kg in females. The lesions produced include degenerative changes and necrosis in the liver, spleen, exocrine and endocrine pancreas, kidney, salivary glands, myocardium and skeletal muscle. An unusual lesion, seen in the bile ducts and other ducts, was enlargement of the nucleus with margination of the chromatin and subsequently enlargement of the cells lining the ducts.
It appears that cyclopiazonic acid produces focal necrosis in most organs at high dosage and at lower dosage affects ducts or organs (such as the islets of Langerhans) originating from ducts. The Sterigmatocystins are related to the aflatoxins and are considered a carcinogen.
Aspergillus fumigatus
Fumigatus readily produces Gliotoxin which has been found on building materials from water affected buildings as well as in dust from similarly affected buildings. Gliotoxin and other agents have been isolated from fumigatus which are ciliotoxic and cause damage to the respiratory epithelium from humans cultured in vitro. Read the paper.
Other mycotoxins produced by fumigatus are: fumagillin, helvolic acid, fumatremorgin A and Asp-hemolysin.
Aspergillus niger
Niger produces Gliotoxin, which has been identified in the sera of humans and mice with aspergillosis.
Aspergillus sydowii
Sydowii is now globally distributed. Ecologically, it is a pathogen of coral and has caused serious damage to coral in the Caribbean and other places. It is unique in that it metabolizes dimethylsulfoniopropionate (a chemical rich in corals to highly toxic dirnethyl sulfide).
In addition, the organism produces mulundocandin, which is an antimycotic agent. Attempts have been made to produce genetically altered strains of A. sydowii in order to obtain mulundocandin for the purpose of treating immune compromised individuals with mycoses.
Aspergillus ochraceus
Ochraceus produces Ochratoxin A and B. Ochratoxin A is nephrotoxic, carcinogenic, immuno-suppressive and is neurotoxic in mice. This species can also produce Penicillic acid.
Aspergillus cistus
Cistus has been shown to produce Sterigmatocystin.
Aspergillus restrictus
Restrictus produces restricrocin which blocks protein synthesis at the level of ribosomes. Arestrictins A and B are dioxopiperazine derivatives and are immunosuppressive.
Aspergillus scieroriorum
This species produces Penicillic acid. Penicillic acid (PA), a carcinogenic mycotoxin, can cause generalized hepatic necrosis in the mouse and cytotoxicity in cultured cells, including hepatocytes.
Aspergillus peniciflioicies
Arestrictins A and B which have been detected from building isolates of this fungus.
Aspergillus parasiticus
This mold produces the following Aflatoxins: G2 G2,B1 & B2.